In Black–Scholes option pricing model, the implied volatility or ‘IV’ of an option contract is the cost embedded in the option of the volatility of the underlying instrument that it is being valued against. Volatility is the input in an option pricing model that measures when an asset will likely return to a theoretical value equal to the current market price of the option strike price.
옵션가격결정모형에서 옵션계약의 내재변동성이나 'IV'는 평가대상인 기초상품의 변동성 옵션에 내재된 원가이다. 변동성은 옵션 가격 모델에서 자산이 옵션 행사가격의 현재 시장 가격에 해당하는 이론적 가치로 복귀할 가능성이 높은 시점을 측정하는 입력물입니다
Implied volatility is a future looking and subjective measurement that is different from the historical volatility of an asset. This is because the historical volatility is calculated from known past returns of a stock, commodity, or market. An option trader must understand where the implied volatility is in terms of the underlying asset, implied volatility rank is a tool used to understand an options implied volatility from a one year high and low implied volatility.
내재변동성은 자산의 과거 변동성과는 다른 미래형 및 주관적 측정치이다. 이는 역사적 변동성이 주식, 상품 또는 시장의 알려진 과거 수익률에서 계산되기 때문입니다. 옵션 거래자는 내재된 변동성이 기초 자산과 관련하여 어디에 있는지를 이해해야 하며, 내재된 변동성 순위는 1년 동안 높고 낮은 내재된 변동성을 나타내는 옵션을 이해하는 데 사용되는 도구이다.
If the implied volatility range is 30 to 60 over the past year. The lowest implied volatility value is 30, and the highest implied volatility value is 60. Compare the current implied volatility value to this range to try to see how the current implied volatility ranks related to its historical implied volatility range. If the current implied volatility value is 45, then this would equal an implied volatility rank of 50% since it is in the middle of this range
암시적 변동성 범위가 지난 1년 동안 30~60인 경우라면. 최저 암묵적 변동성 값은 30이며, 가장 높은 암묵적 변동성 값은 60입니다. 현재 내포된 변동성 순위가 과거 내포된 변동성 범위와 어떻게 관련되는지 확인하기 위하여 현재 내포된 변동성 값을 이 범위와 비교하라. 현재 내포된 변동성 값이 45인 경우, 이 범위의 중간에 있으므로 내포된 변동성 순위가 50%에 해당합니다
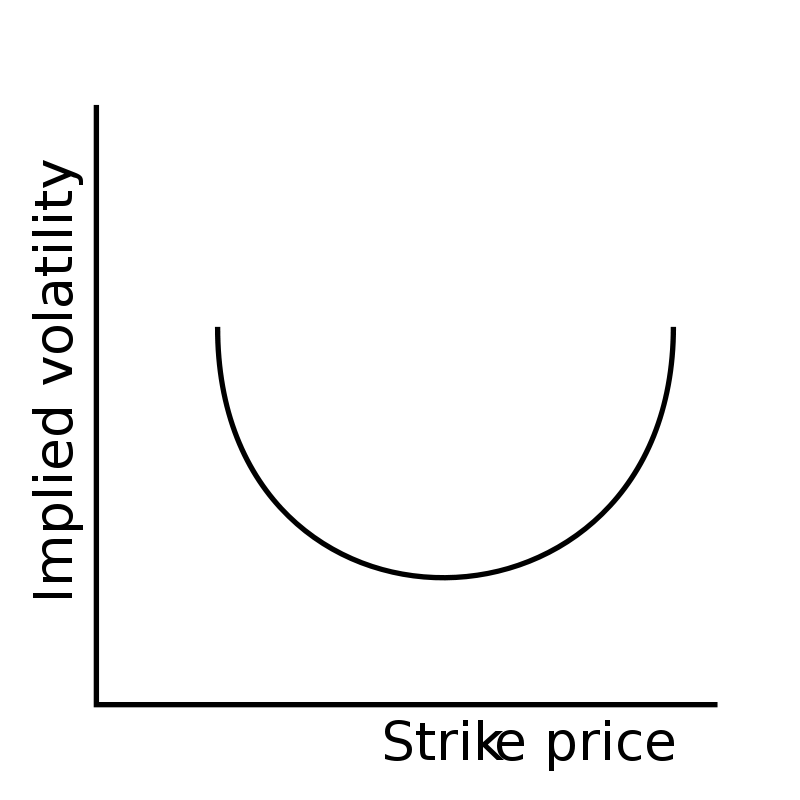
The below image is an example of a ‘volatility smile’ and can be created by implied volatility patterns that form in the prices of option chains. This curving pattern(아래 그림) is correlated to the implied volatility in a market that is needed to modify the Black–Scholes options pricing formula to fit market prices. Options that have strike prices that differ a large amount from the underlying asset’s current price can have much greater prices due to their higher implied volatilities than what would be priced into normal option pricing models. Options with higher prices in relation to at-the-money options are called either deep in-the-money or out-of-the-money. They options have either very high delta (in-the-money) they gain intrinsic value fast or they have very low delta (out-of-the-money) and can grow in price in percentage terms due to gamma with the fast delta expansion, either of these factors make them more expensive based on their implied volatility.
아래 이미지는 '변동성 미소'의 예이며 옵션 체인의 가격에 형성되는 내재된 변동성 패턴을 통해 생성될 수 있다. 이러한 곡률 패턴은 시장 가격에 맞게 Black–Scholes 옵션 가격 책정 공식을 수정하는 데 필요한 시장의 내재적 변동성과 관련이 있습니다. 기본 자산의 현재 가격과 큰 차이가 있는 행사가격이 있는 옵션은 일반적인 옵션 가격 책정 모델보다 암묵적인 볼륨이 높기 때문에 가격이 훨씬 더 높을 수 있습니다. 즉석 옵션(at the money)과 관련하여 가격이 더 높은 옵션을 Deep In-Money 또는 Out-of-Money라고 합니다. 이러한 옵션은 매우 높은 델타(돈 내)를 가지거나 내재가치를 빠르게 얻거나 매우 낮은 델타(돈 외)를 가지며 빠른 델타 확장에 따른 감마(감마)로 인해 백분율 단위로 가격이 상승할 수 있습니다. 이러한 두 가지 요인 중 하나는 내재된 변동성을 바탕으로 가격이 더 비싸집니다.
By Brianegge at English Wikipedia – Transferred from en.wikipedia to Commons by Liftarn using CommonsHelper., Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=12137022