The Cognitive Bias Codex(인식편향 항목)
A cognitive bias is a mental pattern that breaks from logic, reason, and the ability to rationally judge something through the filter of facts and reality. It is when an individual’s thinking is so cloude(흐리게 하다)d by their own subjective reality, memories, and experience that they are unable to interpret new information correctly. A cognitive bias can cause someone to ignore reality in favor of their own preconceived belief system and internal reality. A cognitive bias can take the form of emotional irrationality(비합리성,불합리), inaccurate judgements, and deciding to ignore new facts and information that doesn’t align with a chosen world view.
인지적 편견은 사실과 현실의 여과기를 통해 논리, 이성, 그리고 어떤 것을 합리적으로 판단하는 능력에서 벗어나는 정신적 패턴이다. 개인의 사고가 자신의 주관적인 현실과 기억, 경험에 의해 너무 흐려져 새로운 정보를 올바르게 해석할 수 없을 때이다. 인지적 편견은 누군가 자신의 선입견 체계와 내부 현실에 유리하게 현실을 무시하게 만들 수 있다. 인지적 편견은 감정적 불합리성, 부정확한 판단, 그리고 선택된 세계관과 일치하지 않는 새로운 사실과 정보를 무시하기로 결정하는 형태를 취할 수 있다.
Sometimes cognitive biases are adaptive(적응적) mental models to avoid pain, social rejection, or to continue to hold religious or political beliefs that have already been committed(맡기다) to. They can lead to some strengths in certain situations like stubbornness to reach goals that seemed impossible or a clarity of focus to stay on one path until completion. They can enable fast decisions as little thinking is required when choosing preconceived beliefs. However a cognitive bias can create huge weaknesses and blind spots in knowledge and cause a lack of research with learning and growing as beliefs override the need for seeking the truth.
때때로 인지적 편견은 고통을 피하거나, 사회적 거부감을 피하거나, 이미 헌신한 종교적 또는 정치적 신념을 계속 보유하기 위한 적응적 정신 모델이다. 그들은 불가능해 보이는 목표에 도달하기 위한 완고함이나 완료될 때까지 한 가지 길에 머무르기 위한 집중의 명확함 같은 특정한 상황에서 어떤 강점을 이끌어낼 수 있다. 그들은 선입견을 선택할 때 거의 생각하지 않아도 되기 때문에 빠른 결정을 가능하게 할 수 있다. 그러나 인지적 편견은 지식의 거대한 약점과 맹점을 만들 수 있으며, 믿음이 진리를 추구할 필요를 우선시함에 따라 학습과 성장에 대한 연구 부족을 야기할 수 있다.
They can be identified in many different ways.
그것들은 많은 다른 방법으로 식별될 수 있다.
Examples of basic cognitive biases include:
기본적인 인지 편향의 예는 다음과 같다.
A bias can be directed(향하다) at specific groups of people instead of looking at each member as an individual person.
편향은 각 구성원을 개인으로 보지 않고 특정 그룹의 사람들을 향할 수 있다.
A bias can affect proper decision-making on something you already possess due to sunk(매몰) costs fallacy.
편향은 매몰 비용 오류로 인해 당신이 이미 가지고 있는 어떤 것에 대한 적절한 의사결정에 영향을 미칠 수 있다.
A bias can cause a person to be fooled(속다) by randomness by seeing unrelated correlation in patterns that are coincidence.(우연의 일치)
치우침은 우연인 패턴에서 관련 없는 상관관계를 보고 무작위에 속게 할 수 있다.
A consistency bias can have an affect on memory making you think you were the same in the past as you are today.
일관성 편향은 과거의 자신이 현재와 같았다고 생각하게 하는 기억력에 영향을 줄 수 있다 ,
An egocentric bias can cause the rejection or denial of personal negative feedback when a person holds a belief in a positive self image so blindly that it is protected from new information that doesn’t fit the ego filter.
자기중심적 편향은 사람이 맹목적으로 긍정적인 자아 이미지에 대한 신념을 가지고 있어 그것이 자아 필터에 맞지 않는 새로운 정보로부터 보호를 받아 받을 때 개인적인 부정적인 피드백의 거부나 부정의 인이 될 수 있다.
Many biases cause people to ignore new information, feedback, facts, and reality.
많은 편견들은 사람들로 하여금 새로운 정보, 피드백, 사실, 그리고 현실을 무시하게 만든다.
Some biases cause a decision to be affected by things that do not matter.
어떤 편견은 중요하지 않은 것들에 의해 영향을 받는 결정의 원인이 된다
The framing effect will cause a similar problem to have different actions to respond to it depending on how it is understood in different contexts, during different moods, or who it effects.
프레임 효과는 유사한 문제가 다른 맥락에서 다른 분위기 동안 누구에게 효과가 있는가를 어떻게 이해되어지는가에 따라 반응을 할 다른 행동을 가지는 유사한 문제의 원인이 됩니다 .
(레임효과는 누구에게 효과각 있으며 분위기에 따라서 문맥상 이해되는 방법에 따라서 반응하는 행동을 가지는 유사한 제를 유발하게 한다 )
The distinction bias causes decisions that are made at one time to have different choices than if they are made separately at different times and in different individual situations.
구별 편향은 한 번에 이루어진 결정이 다른 시간이나 다른 개별 상황에서 별도로 이루어지는 경우와는 다른 선택을 하게 한다.
The anchoring effect gives more meaning to a less important part of a problem just because it happened more recently in a chain of events.
앵커링 효과는 단지 일련의 사건에서 더 최근에 발생했다는 이유만으로 문제의 덜 중요한 부분에 더 많은 의미를 부여한다.
Beware of cognitive biases as they are the biggest causes of making less than ideal decisions in situations as they filter facts and information through a very limited decision making process. Developing the mental and emotional equanimity(침작함) to see above your own preconceived beliefs, experiences, ego, fears, and greed is a super power.
인지 편향은 매우 제한된 의사 결정 과정을 통해 사실과 정보를 걸러내기 때문에 상황에서 이상적이지 않은 결정을 내리는 가장 큰 원인이므로 주의하십시오. 자신의 선입견, 경험, 자아, 두려움, 탐욕 이상의 것을 볼 수 있는 정신적, 감정적 평정심을 기르는 것은 초능력이다.
Below is a list of 188 cognitive biases, grouped into categories and rendered(제시하다)y John Manoogian III.
아래는 188개의 인지 편향 목록을 분류하여 John Manoogian III에 의해 렌더링되었다.
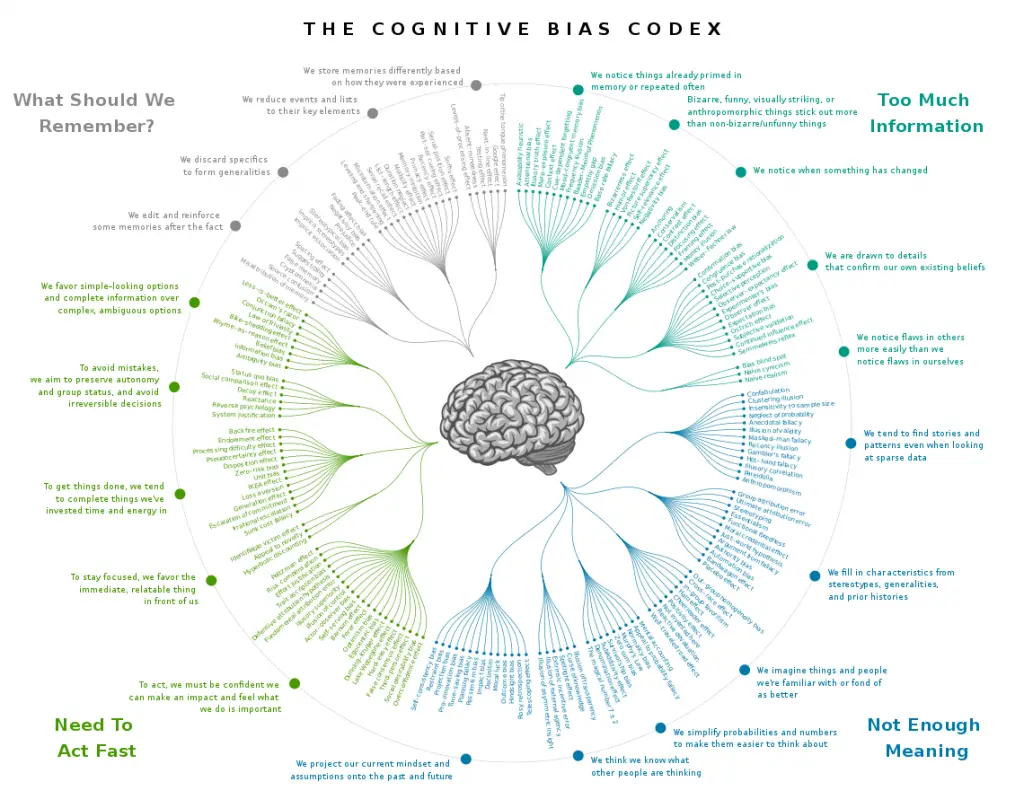
design: John Manoogian III categories and descriptions: Buster Benson implementation: TilmannR / CC BY-SA (https://creativecommons.org/licenses
'거래기술에 관한 정보' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Things That a Backtest Does Not Show:(백테스트가 보여주지 않는 것들:) (0) | 2020.05.02 |
|---|---|
| Never Catch A Falling Knife(떨어지는 칼을 절대 잡지 마십시오) (0) | 2020.05.01 |
| If Buddha was a Trader:(만일 부처님께서 거래자라면) (0) | 2020.04.29 |
| Is Technical Analysis BS?(기술 분석은 BS인가?) (0) | 2020.04.29 |
| Top 10 Educational Finance Documentaries on Netflix:(넷플릭스의 교육 금융 다큐멘터리 10위:) (0) | 2020.04.29 |